GCP Marketplace Nodes
Deploy blockchain nodes without the need to install dependencies or manage configuration files. The nodes come with a copy of the databases locally which drastically reduces bootstrap times. The machine images are available for Flare Mainnet, Flare Testnet Coston2, Songbird Canary-Network, Songbird Testnet Coston and several other networks.
Head to Google Cloud Marketplace to get started.
Supported blockchain nodes
| Name | Config Dir | Machine Type | vCPUs | RAM | Disk Size | Disk Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flare Mainnet | /etc/flare | n2d-standard-4 | 4 | 16 GB | 830 GB | Balanced |
| Flare Mainnet Rosetta | /etc/flare_rosetta | n2d-standard-4 | 4 | 16 GB | 830 GB | Balanced |
| Flare Testnet Coston2 | /etc/coston2 | n2d-standard-4 | 4 | 16 GB | 280 GB | Balanced |
| Flare Testnet Coston2 Rosetta | /etc/coston2_rosetta | n2d-standard-4 | 4 | 16 GB | 280 GB | Balanced |
| Songbird Canary-Network | /etc/songbird | n2d-standard-8 | 8 | 32 GB | 2,730 GB | Balanced |
| Songbird Testnet Coston | /etc/coston | n2d-standard-4 | 4 | 16 GB | 280 GB | Balanced |
Other supported networks
| Name | Config Dir | Machine Type | vCPUs | RAM | Disk Size | Disk Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorand | /etc/algorand | e2-custom-8-13056 | 8 | 13 GB | 70 GB | Balanced |
| Avalanche | /etc/avalanche | e2-custom-8-16384 | 8 | 16 GB | 530 GB | Balanced |
| Bitcoin | /etc/bitcoin | e2-custom-2-16128 | 2 | 16 GB | 1,030 GB | Balanced |
| Binance Smart Chain | /etc/bsc | c2-standard-8 | 8 | 32 GB | 2,030 GB | SSD |
| Cosmos Hub | /etc/cosmos | n2d-standard-4 | 4 | 16 GB | 1,030 GB | Balanced |
| Dogecoin | /etc/dogecoin | e2-custom-2-11008 | 2 | 11 GB | 380 GB | Balanced |
| Ethereum | /etc/ethereum | n2d-standard-8 | 8 | 32 GB | 2,230 GB | Balanced |
| Ethereum Holesky | /etc/ethereum | n2d-standard-8 | 8 | 32 GB | 430 GB | Balanced |
| Ethereum Sepolia | /etc/ethereum | n2d-standard-8 | 8 | 32 GB | 730 GB | Balanced |
| Filecoin Lotus | /etc/filecoin | e2-custom-16-32768 | 16 | 32 GB | 1,030 GB | SSD |
| Litecoin | /etc/litecoin | e2-custom-2-11520 | 2 | 12 GB | 330 GB | Balanced |
| Polygon | /etc/polygon | n2d-standard-16 | 16 | 64 GB | 6,030 GB | SSD |
| XRPL | /etc/xrpl | n2d-standard-8 | 8 | 32 GB | 375 GB | Local SSD |
Prerequisites
Ensure you have:
-
A Google Cloud account
-
A service account with at least the following permissions (it can be created beforehand or during the launch process using GUI):
- roles/config.agent
- roles/compute.admin
- roles/iam.serviceAccountUser
-
Verify that your Quotas and System Limits, located in IAM and admin > Quotas and system limits, meet the resource requirements for the blockchain node you intend to deploy. Refer to the Supported blockchain nodes table for the specific resource requirements of each node. Adjust your quotas as needed to ensure sufficient resources are available.
Setup a node
-
Locate and launch the blockchain machine image
Head to the Google Cloud Marketplace.
Click the Launch button to proceed.
-
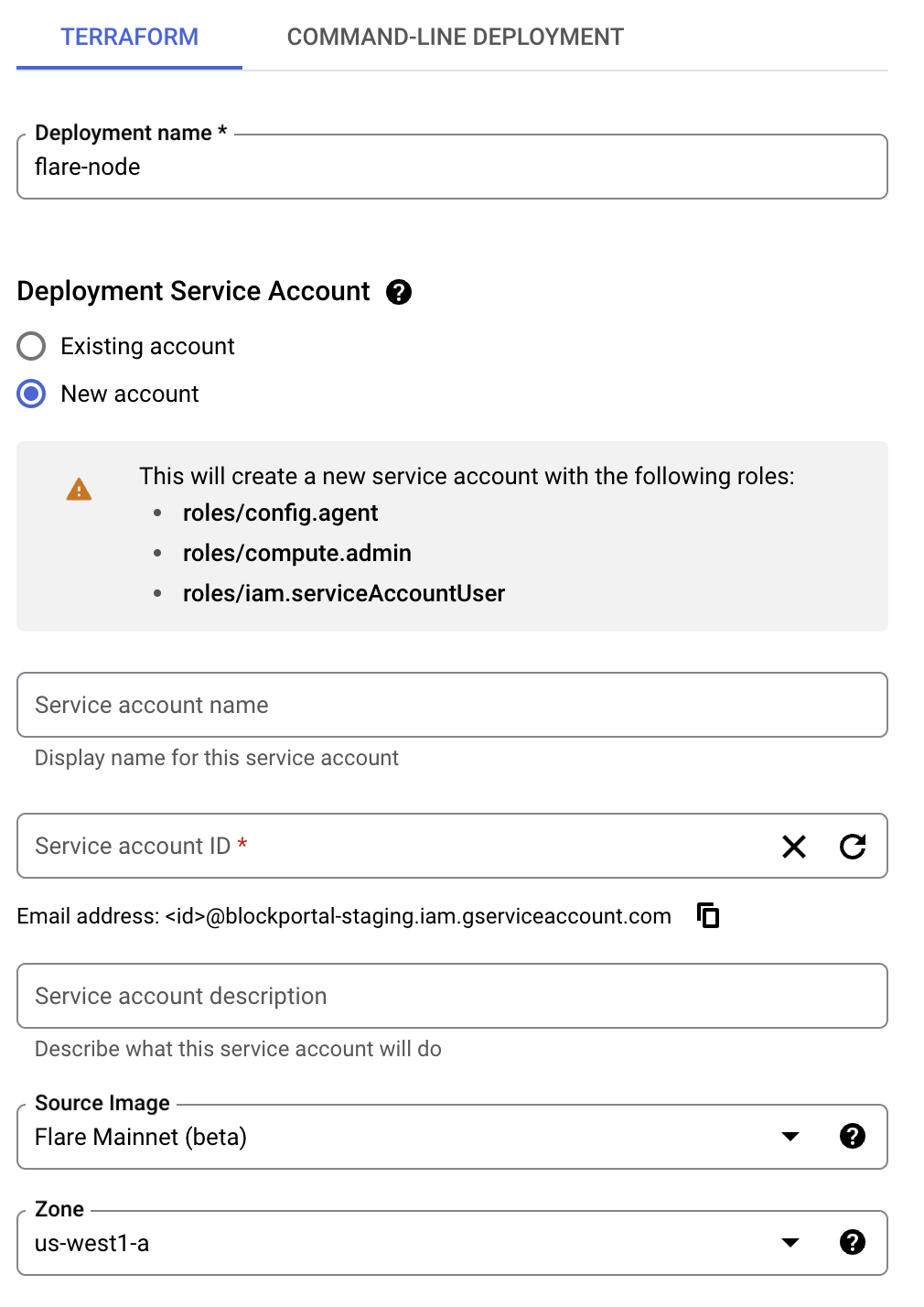
Configure basic settings
Choose the service account, source image, and region for your instance. To use an existing service account, click the Existing account button.
Next, select the network where the node will be deployed, and configure basic firewall rules. Once done, click Deploy. This will launch a node with the deployment name, for example
flare-node, in the Compute Engine > VM instances.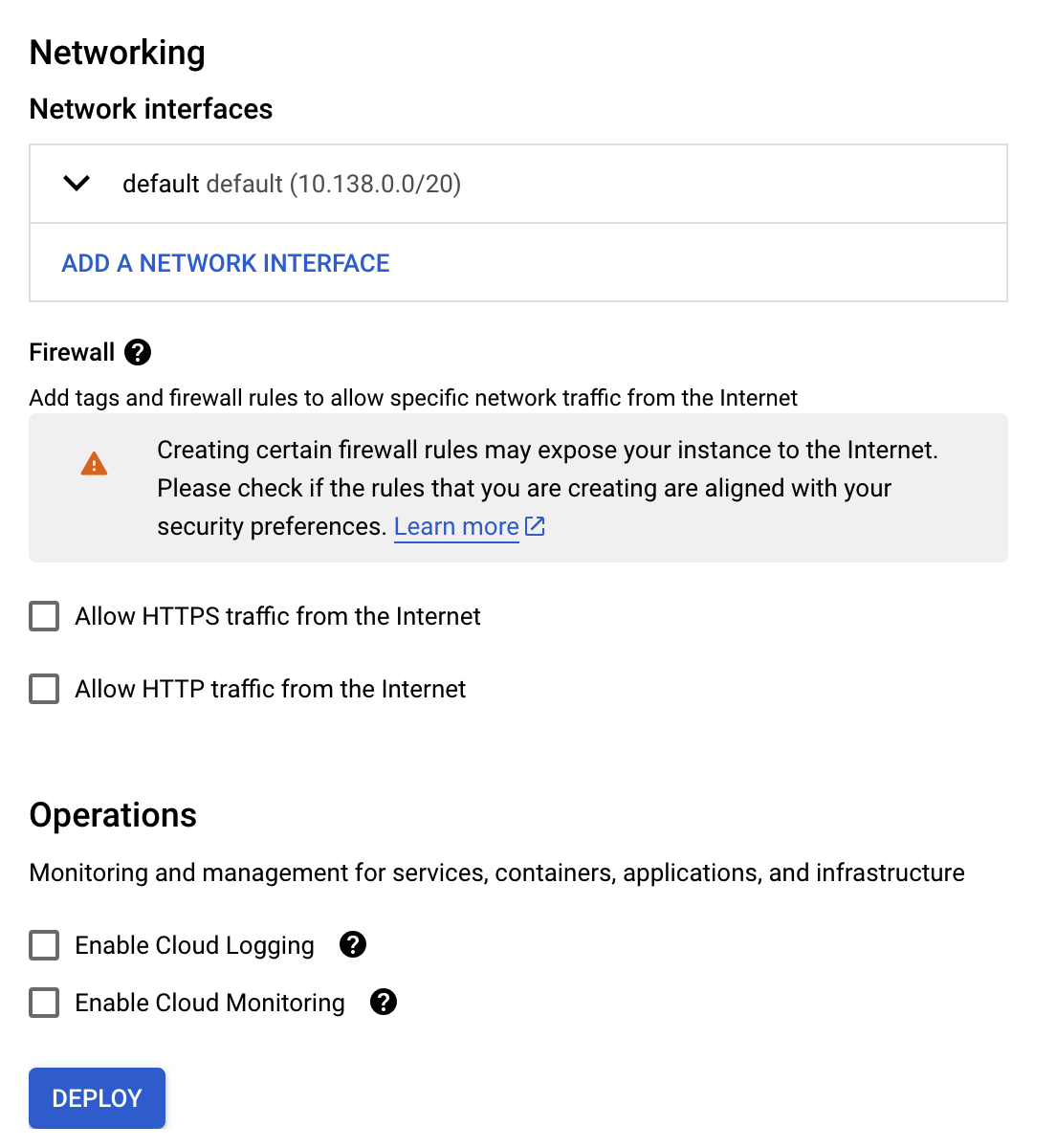
-
Troubleshooting
If you encounter any issues during the deployment process, refer to the Troubleshooting Section for guidance.
Connect to the node
Node operations are managed using the nodectl CLI tool.
sudo nodectl help
Configuration files are located in the /etc/<node_name> directory. For instance, Flare nodes will have their configurations in /etc/flare.
To start the node, connect to the instance and apply the services using:
# Applies all services configured in `/etc/<node_name>/config.yaml`
sudo nodectl apply --target all
Verify node operation
The quickest way to verify that the node is running is by using the built-in health checks.
Logs can also be accessed in the /var/log/<node_name> directory, for example, /var/log/flare.
# Run health checks
sudo nodectl health
# Display detailed node information
sudo nodectl status
For live log monitoring, use nodectl:
sudo nodectl logs -f
For more log options, refer to the journalctl manual:
man journalctl
Advanced Deployment with Terraform
Blockchain machine images can also be deployed using Terraform to meet advanced requirements, such as replicating nodes, automating configuration, and scaling.
In this section, we provide an example which deploys two replicas of Flare nodes in the EU and US regions. Source code is available in the flare-foundation/bmi-terraform-examples repository.
The first step is to obtain the latest blockchain machine image.
Start by navigating to the Google Cloud Marketplace and click LAUNCH.
Then, switch to the COMMAND-LINE DEPLOYMENT tab and scroll down to the VM Image section, where you will find a table containing the latest images.
Copy the name of the latest image and update the locals in the instance.tf file accordingly.
Additionally, ensure that all required variables are correctly set in the terraform.tfvars, such as GCP project name, before proceeding.
locals {
replicas = {
1 = {
# update here
image = "projects/mpi-flare-public/global/images/flare---v1-..."
zone = "europe-west1-c"
},
2 = {
# update here
image = "projects/mpi-flare-public/global/images/flare---v1-..."
zone = "us-west1-a"
}
}
}
Next, configure a firewall rule to allow external traffic from other peers in the network to access port 9651.
resource "google_compute_firewall" "peering" {
project = var.gcp_project_name
name = "flare-example-peering-tcp"
network = "default"
allow {
protocol = "tcp"
ports = ["9651"]
}
source_ranges = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
target_tags = ["flare-example-peering"]
priority = "600"
}
Optionally, you can create a service account with the necessary permissions to access a Slack webhook stored in GCP Secret Manager. The node uses the secret's name to obtain the webhook and sends health alerts to Slack.
Each instance must define both startup and shutdown scripts.
The startup script handles node configuration tasks, such as enabling Promtail log scraping, node metrics, and Slack alerts.
Use tools such as jq, yq and sed to perform the configuration.
#!/bin/bash
#### Configure node ####
# Example
yq eval '.health_checks.slack_alerts.webhook_secret_name = "example_slack_webhook_secret_name"' -i /etc/flare/config.yaml
yq eval '.health_checks.slack_alerts.enabled = true' -i /etc/flare/config.yaml
#### Start node ####
nodectl apply --target all
The shutdown script ensures the node shuts down gracefully.
#!/bin/bash
nodectl stop
Finally, all the previously mentioned files and resources are used to define instance resources, which tie together the configuration, scripts, replication and permissions necessary for the node deployment.
resource "google_compute_instance" "this" {
for_each = local.replicas
project = var.gcp_project_name
name = "flare-node-example-replica-${each.key}"
zone = each.value.zone
machine_type = "n2d-standard-4"
metadata = {
startup-script = templatefile("${path.module}/templates/startup.sh", {})
shutdown-script = templatefile("${path.module}/templates/shutdown.sh", {})
}
boot_disk {
initialize_params {
image = each.value.image
type = "pd-balanced"
}
}
network_interface {
network = "default"
access_config {
// Ephemeral public IP
}
}
tags = google_compute_firewall.peering.target_tags
service_account {
email = google_service_account.this.email
scopes = ["cloud-platform"]
}
}
Troubleshooting
-
Deployment via UI failure due to Terraform state lock
- Symptom: The deployment fails, and clicking Retry leads to Terraform state lock errors.
- Solution: Instead of retrying, delete the failed deployment and start a new one.
-
Deployment failure due to exceeded quotas
- Symptom: The deployment fails, displaying an error message in the logs similar to:
Error: Error waiting for instance to create: Quota 'SSD_TOTAL_GB' exceeded. Limit: 500.0 in region us-west1.
metric name = compute.googleapis.com/ssd_total_storage
limit name = SSD-TOTAL-GB-per-project-region
limit = 500
dimensions = map[region:us-west1] - Solution: Resource quotas need to be increased manually. To do this, refer to the Quotas and System Limits documentation and navigate to IAM & Admin > Quotas. After adjusting the quotas, delete the failed deployment and deploy a new one.
- Symptom: The deployment fails, displaying an error message in the logs similar to: